
Sep. 25, 2025
Welcome to IDEAL's ultimate guide to Understanding the Difference Between PC and PMMA: Acrylic vs. Polycarbonate. Our blog is a comprehensive resource for anyone interested in learning more about this versatile and affordable option.
In today's manufacturing landscape, selecting the right plastic material is crucial for creating high-quality, durable products. PMMA, polycarbonate, and acrylic are three popular transparent plastics widely used across various industries. This article delves into their differences, applications, and machining processes, helping industrial designers, product developers, and researchers make informed decisions for their projects.
What is PMMA?
PMMA (Polymethyl methacrylate), commonly known as acrylic, is a transparent thermoplastic often used as a lightweight or shatter-resistant alternative to glass. Renowned for its excellent optical clarity and UV resistance, PMMA is a preferred choice for applications requiring transparency and durability.

Properties of PMMA
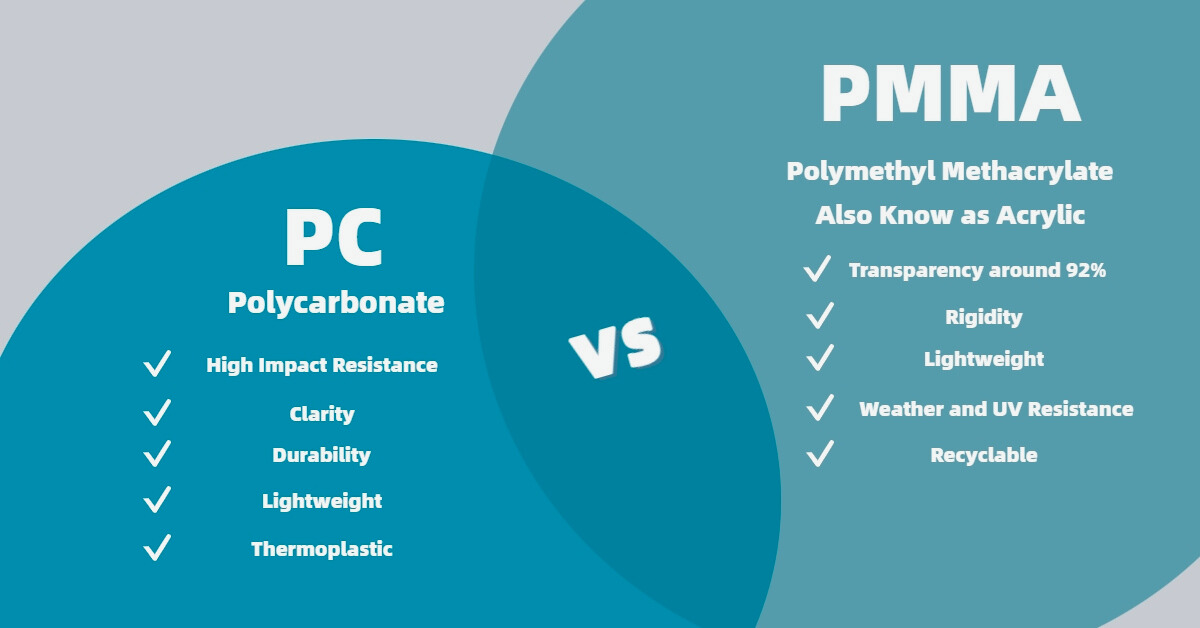
Transparency: PMMA offers up to 92% light transmission, making it ideal for display cases and lighting covers.
UV Resistance: It resists yellowing and degradation under prolonged UV exposure.
Machinability: PMMA can be easily machined, allowing for precise manufacturing of intricate parts.
Polycarbonate vs. PMMA: Key Differences
While both polycarbonate and PMMA are transparent plastics, they exhibit distinct differences that influence their suitability for specific applications.
Impact Resistance
Polycarbonate stands out with its exceptional impact resistance, being 9-31 times stronger than PMMA. This makes polycarbonate ideal for applications where durability and safety are paramount, such as in automotive parts and protective gear.
Optical Clarity
PMMA surpasses polycarbonate in terms of optical clarity, offering higher light transmission. This makes PMMA the go-to material for applications like lenses, light fixtures, and display screens where superior clarity is essential.
Thermal Stability
Polycarbonate exhibits better thermal stability compared to PMMA. It can withstand higher temperatures without deforming, making it suitable for applications exposed to heat.
Acrylic: A Versatile Transparent Plastic
Acrylic is synonymous with PMMA but often refers to the broader category of acrylic-based plastics. Its versatility makes it a favorite among product designers and manufacturers.

Advantages of Acrylic
Lightweight: Acrylic is significantly lighter than glass, reducing transportation and handling costs.
Customization: It can be easily colored, textured, and molded into various shapes.
Cost-Effective: Acrylic is generally more affordable than polycarbonate, making it a cost-effective choice for many projects.
Common Uses of Acrylic
Acrylic is widely used in signage, aquarium tanks, and architectural elements due to its clarity and ease of fabrication.
Choosing the Right Plastic Material
Selecting between PMMA, polycarbonate, and acrylic depends on the specific requirements of your project. Consider the following factors:
Strength and Durability: Choose polycarbonate for high-impact applications.
Optical Clarity: Opt for PMMA when maximum transparency is needed.
Cost and Availability: Acrylic often provides a balance between cost and performance.
CNC Machining Comparison: PMMA vs. Polycarbonate
| Property / Feature | PMMA (Polymethyl Methacrylate / Acrylic) | Polycarbonate (PC) |
|---|---|---|
| Machinability | Easy to machine — cuts cleanly and smoothly with sharp tools | More difficult — tougher and may require slower cutting speeds |
| Surface Finish Quality | Excellent — highly polished, optical-grade surface achievable directly after machining | Good — can be polished but usually needs more post-processing |
| Transparency After Machining | Very high (~92%), retains excellent optical clarity | Slightly lower (~88–90%), may have minor haze after machining |
| Edge Finish | Clean edges, can achieve glass-like clarity after polishing | Edges may appear rough or stress-whiten; polishing often required |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate — more brittle and prone to cracking during machining | Excellent — highly impact resistant and less likely to crack |
| Scratch Resistance | Higher — naturally more scratch-resistant than PC | Lower — more prone to surface scratches |
| Thermal Resistance (During Machining) | Lower (~100 °C softening point) — risk of melting if tool speed is too high | Higher (~135 °C softening point) — better heat resistance under cutting |
| Tool Wear | Low — gentle on tools | Higher — tougher material increases tool wear over time |
| Dimensional Stability / Tolerance | Excellent — minimal warping or deformation | Good — but may stress-relieve or warp slightly if overheated |
| Bonding / Assembly (After Machining) | Easy to bond with solvents or adhesives | Requires specialized adhesives for strong joints |
| Cost (Material + Machining) | Lower | Higher |
| Best Use Cases | Optical lenses, light guides, display covers, transparent prototypes | Functional mechanical parts, enclosures, protective covers, impact-resistant components |
Machining of Polycarbonate
Machining polycarbonate requires specific techniques to maintain its integrity and optical clarity. Proper machining ensures that polycarbonate parts are precise and free from defects.

Best Practices for Machining Polycarbonate
Tool Selection: Use sharp, high-speed steel or carbide tools to reduce heat buildup.
Cooling: Employ cooling methods like air or liquid coolant to prevent melting and warping.
Feed Rate: Maintain an optimal feed rate to achieve smooth surfaces and precise dimensions.
Common Machining Processes
CNC Milling: Ideal for creating intricate shapes and precise dimensions.
Laser Cutting: Provides clean edges and high accuracy for detailed designs.
Drilling and Tapping: Facilitates the creation of threaded holes without compromising material strength.
Applications of PMMA Parts
PMMA parts find applications across various industries due to their transparency and ease of fabrication.
Industries Using PMMA Parts
Automotive: Headlight lenses and instrument panels.
Medical: Light covers for medical devices and equipment housings.
Consumer Electronics: Display screens and protective covers.
Polycarbonate Parts: Benefits and Uses
Polycarbonate parts are favored for their strength and durability, making them suitable for demanding applications.
Benefits of Polycarbonate Parts
High Impact Resistance: Suitable for environments where parts are subject to shocks and impacts.
Thermal Stability: Maintains structural integrity under high temperatures.
Lightweight: Reduces the overall weight of products without compromising strength.
Uses of Polycarbonate Parts
Automotive: Bumpers, headlights, and interior components.
Aerospace: Aircraft windows and structural components.
Safety Equipment: Helmets and protective visors.
Acrylic and Polycarbonate in Product Design
Integrating acrylic and polycarbonate in product design enhances functionality and aesthetics. Designers leverage the unique properties of each material to create innovative products.
Designing with Acrylic
Acrylic’s clarity and versatility make it ideal for creating visually appealing products. Its ease of coloring and shaping allows designers to experiment with different aesthetics.
Designing with Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate’s strength and thermal stability are essential for products that require durability and performance. It’s often used in structural components and products exposed to harsh conditions.
Common Plastic Types in Manufacturing
Beyond PMMA, polycarbonate, and acrylic, several other plastic types are prevalent in manufacturing:
Table: Common Plastic Types and Their Properties
| Plastic Type | Full Name | Key Properties | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABS | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene | Tough, good impact resistance, machinable, moderate cost | Automotive parts, enclosures, toys (e.g., LEGO) |
| PMMA (Acrylic) | Polymethyl Methacrylate | Excellent transparency (92%), rigid, scratch-resistant, brittle | Lenses, light covers, display cases |
| PC | Polycarbonate | Very high impact resistance, transparent (~88–90%), less scratch resistant, good heat resistance | Safety glasses, machine guards, helmets |
| PE (HDPE/LDPE) | Polyethylene (High/Low Density) | Lightweight, excellent chemical resistance, flexible (LDPE), tough (HDPE) | Bottles, containers, piping, films |
| PP | Polypropylene | Low density, chemical resistant, fatigue resistant (living hinges), semi-rigid | Automotive parts, packaging, medical disposables |
| PVC | Polyvinyl Chloride | Rigid or flexible, chemical resistant, flame retardant, inexpensive | Pipes, cables, flooring, medical tubing |
| PA (Nylon) | Polyamide | Strong, abrasion resistant, self-lubricating, absorbs moisture | Gears, bearings, mechanical components |
| POM (Acetal/Delrin) | Polyoxymethylene | High stiffness, low friction, good dimensional stability | Precision parts, gears, bushings |
| PTFE (Teflon) | Polytetrafluoroethylene | Excellent chemical resistance, very low friction, high heat resistance | Seals, gaskets, non-stick coatings |
| PET | Polyethylene Terephthalate | Transparent, good strength, chemical resistance, recyclable | Bottles, food containers, fibers (polyester) |
Conclusion
For more information on PMMA parts with IDEAL, visit our Polycarbonate Truck Bushing Factory page. Explore our range of polycarbonate bushings for truck to find the perfect fit for your vehicle. Need assistance with choosing the right material? Check out our Plastic Material Guide for detailed insights.
Contact IDEAL whenever you need help assessing the manufacturability of your product designs.

Search Blog

Hey there, I'm Abby!
At IDEAL RAPID PRODUCTION, I'm a Project Management Expert in custom manufacturing field for more than 15 years. We offer cost-effective machining services from China. Ask for a quote for your ongoing or upcoming projects now!


Aluminum Extrusion Design Guide
Dec. 29, 2025


GET IN TOUCH WITH US
Navigation
RESOURCE
Contact Us
Tel: 0755-36957776
E-mail: info@idealrp.com
Skype: +86 135 2877 3620
Whatsapp: +86 135 2877 3620
Add.: Shenghua Building, Songgang, Bao'an,Shenzhen 518105
Add.: Room 4, 16/F, Ho King Commercial Building, 2-16 Fa Yuen Street, Mong Kok, Kowloon, Hong Kong
